Atmospheric science explores the Earth's atmosphere and its processes. It helps us understand weather patterns, climate change, and air quality.
This field studies everything from the air we breathe to the forces shaping our planet's climate. Atmospheric science is vital in predicting storms, managing natural resources, and protecting our environment. It combines physics, chemistry, and meteorology to offer insights into atmospheric phenomena.
With the increasing impact of climate change, this science is more important than ever. By studying atmospheric science, we can better prepare for weather events and reduce environmental harm. Dive into this fascinating field to learn how it affects our daily lives and the world around us.
Credit: en.citizendium.org
Introduction To Atmospheric Science
The atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding Earth. It protects us from harmful solar radiation. The atmosphere also keeps our planet warm. Without it, life on Earth would not exist.
This layer contains oxygen we need to breathe. It also holds moisture for rain. The atmosphere helps us in many ways.
Studying the atmosphere helps us understand weather patterns. It can tell us about climate change. Knowing more about the atmosphere can save lives during natural disasters.
Research can also help us predict future weather. This knowledge is important for farming and other activities. The more we know, the better we can protect our environment.
Layers Of The Atmosphere
The troposphere is the closest layer to the Earth. It extends up to about 12 kilometers. This layer has most of our weather. Airplanes often fly here. It is where we live.
The stratosphere is above the troposphere. It reaches up to 50 kilometers. The ozone layer is in the stratosphere. It protects us from the sun's harmful rays. Jets and balloons fly in this layer.
The mesosphere is the third layer. It goes up to 85 kilometers. This layer is where meteors burn up. It is the coldest layer of the atmosphere.
The thermosphere is above the mesosphere. It extends up to 600 kilometers. This layer is very hot. The auroras happen here. It also contains the International Space Station.
The exosphere is the outermost layer. It merges with space. The air is very thin here. Satellites orbit in the exosphere. It extends up to 10,000 kilometers. It is the edge of our atmosphere.
Atmospheric Composition
The atmosphere has many gases. The most common gas is nitrogen. It makes up 78% of the air. Oxygen is the next most common. It forms 21% of the air. Other gases are in small amounts. These include argon and carbon dioxide. These gases are important for life. They help plants grow. They keep the Earth warm.
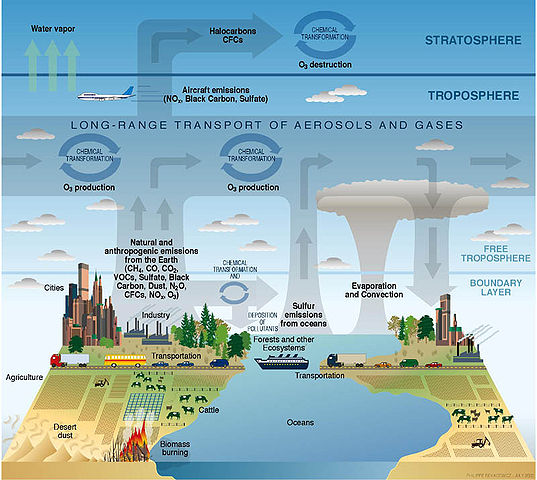
Aerosols are tiny particles in the air. They come from dust, smoke, and salt. Volcanic eruptions add aerosols too. These particles can affect our health. They can make it hard to breathe. They also affect the weather. They can block sunlight. This can cool the Earth. Particulates are solid or liquid particles. They include soot and pollen. They also affect air quality. It's important to understand aerosols and particulates. They impact our daily lives.
Weather Vs. Climate
Weather is the day-to-day conditions. It changes often. It includes temperature, rain, and wind. Climate is the average weather over many years. It changes very slowly. Weather can be sunny today but rainy tomorrow. Climate tells us what to expect over a season or year.
Weather affects our daily choices. It influences what we wear and our outdoor plans. Strong weather events can damage homes and roads. Climate affects farming and water supply. Long-term climate changes can impact food production. Both weather and climate are important to our lives.
Meteorological Phenomena
Clouds form when water vapor rises into the sky. The vapor cools and condenses. Tiny water droplets or ice crystals come together. These droplets group to make clouds. The sky can have different types of clouds. Each type has its own shape and size.
Precipitation happens when clouds get too heavy. They release water back to Earth. This can be rain, snow, sleet, or hail. The weather decides what type we get. Warm weather brings rain. Cold weather brings snow. Sleet and hail need very cold air.
Storms are strong weather events. They can bring heavy rain and strong winds. Thunder and lightning often come with storms. Hurricanes are large storms that form over warm ocean water. They have very strong winds. Hurricanes can cause a lot of damage. They lose strength over land.

Credit: grad.rutgers.edu
Climate Change And Global Warming
Humans cause many changes in the climate. Factories and cars release carbon dioxide into the air. This gas traps heat from the sun. As a result, the planet gets warmer. Cutting down trees also adds to the problem. Trees absorb carbon dioxide. Without trees, more gas stays in the air. Pollution from farms and other activities also hurts the air. These actions make the climate change faster.
Global warming has many long-term effects. Ice melts at the poles, causing sea levels to rise. Coastal areas may flood. This can harm people and animals. Weather patterns may change. Some places may get more rain, others less. This can lead to droughts or floods. Plants and animals may struggle to survive. Some species may even go extinct. The changes can also impact our food and water supply. It's a big problem that needs our attention.
Atmospheric Research Methods
Ground-based observations are vital for studying the atmosphere. Scientists use weather stations, radiosondes, and lidar. These tools measure temperature, humidity, and wind speed. Data helps predict weather and understand climate change. Observations are continuous and reliable.
Satellites help monitor the atmosphere from space. They provide data on cloud cover, sea surface temperatures, and pollution levels. Images and data are collected globally. This helps in accurate weather forecasting. Satellites work day and night. They cover large areas quickly. Data is used for research and disaster management.

Credit: www.eaps.purdue.edu
Future Of Atmospheric Science
New tools are helping scientists study the atmosphere. Drones can now collect data from the sky. This data helps predict the weather better. Satellites take pictures of Earth from space. These pictures show changes in the weather. Computers are also faster now. They can process huge amounts of data quickly. This helps make accurate weather forecasts. Sensors are put in many places. They measure things like temperature and humidity. These tools make our weather predictions more reliable.
Many fields work together to study the atmosphere. Meteorologists study weather patterns. Oceanographers study the seas. The seas affect the weather a lot. Biologists study how plants and animals react to weather changes. Geologists study the Earth's surface. All these experts share their knowledge. Working together gives us a better understanding. It helps us know how our planet works. This teamwork is very important for future research.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Atmospheric Science?
Atmospheric science studies the Earth's atmosphere and its processes. It includes weather forecasting, climate change, and air quality. Researchers analyze atmospheric patterns to understand environmental changes.
How Does Atmospheric Science Impact Climate?
Atmospheric science helps us understand climate change by studying atmospheric patterns. It identifies causes of global warming and predicts future climate trends. This knowledge guides climate policy.
Why Is Atmospheric Science Important?
Atmospheric science is crucial for predicting weather and understanding climate change. It helps in disaster preparedness and environmental protection. It also contributes to sustainable development.
What Tools Do Atmospheric Scientists Use?
Atmospheric scientists use satellites, weather radars, and computer models. These tools help in data collection and analysis. They provide accurate weather forecasts and climate predictions.
Conclusion
Atmospheric science reveals the secrets of our skies. It helps us understand weather patterns. This knowledge assists in predicting storms and managing climate change. Scientists study air, water, and Earth's surface. They work to protect our planet. Everyone benefits from this research.
It keeps us informed and safe. Stay curious about the atmosphere. It affects us all daily. Keep learning and appreciate this vital science.
.png)






0 Comments