Renewable energy relies on physics principles to harness natural resources. Understanding physics helps improve energy efficiency.
Physics plays a crucial role in renewable energy. From wind turbines to solar panels, physics principles are at the core of these technologies. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into mechanical energy. Solar panels transform sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells.
These technologies depend on understanding energy transfer, forces, and motion. By applying physics, we can create more efficient and sustainable energy solutions. This blog explores the fascinating world of physics in renewable energy, showing how scientific principles drive innovation. Join us as we delve into the science behind cleaner, greener energy sources.

Credit: link.springer.com
Introduction To Renewable Energy
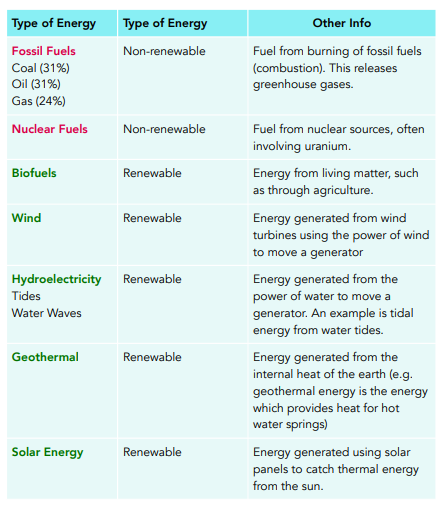
Renewable energy is a critical focus in today’s world. It harnesses natural processes that replenish constantly. This type of energy is sustainable and less harmful to our planet. Common sources include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal. Understanding the physics behind renewable energy helps us utilize these resources efficiently.
Importance Of Sustainability
Sustainability means meeting our needs without harming future generations. Renewable energy plays a significant role in this. Fossil fuels are finite and their use harms the environment. They release greenhouse gases, leading to climate change. Renewable energy sources are cleaner. They produce little or no greenhouse gases. This helps reduce our carbon footprint. We can rely on them indefinitely.
Global Energy Demand
Energy demand is rising worldwide. The growing population and industrial activities drive this increase. Traditional energy sources struggle to meet this demand. They are depleting fast. Renewable energy offers a solution. It can cater to growing needs sustainably. Solar and wind energy are abundant. They can be harnessed almost anywhere. Transitioning to renewables is crucial for our energy future.
Credit: studymind.co.uk
Basic Physics Of Renewable Energy
Understanding the basic physics behind renewable energy is crucial. It helps us grasp how these systems work and their potential to power our future. Let's dive into some core concepts.
Energy Conversion Principles
Energy conversion is a fundamental principle in renewable energy. It involves transforming natural energy sources into usable forms.
Solar panels, for example, convert sunlight into electricity. Wind turbines change wind energy into mechanical power.
Have you ever wondered how a simple gust of wind turns into power for your home? It's all about harnessing nature's energy efficiently.
Efficiency And Losses
Efficiency is key in renewable energy systems. It measures how well energy is converted without waste.
There are always losses during conversion. Solar panels lose some energy as heat, while wind turbines may not capture all wind energy.
Imagine a solar panel on a cloudy day—it won't be as efficient as on a sunny day. How can we improve this?
Improving efficiency means more power with less waste. It’s a constant challenge for scientists and engineers.
Think about your daily energy use. Could renewable sources meet your needs efficiently?
Understanding these principles helps you appreciate the potential and challenges of renewable energy. What steps can you take to support this green shift?
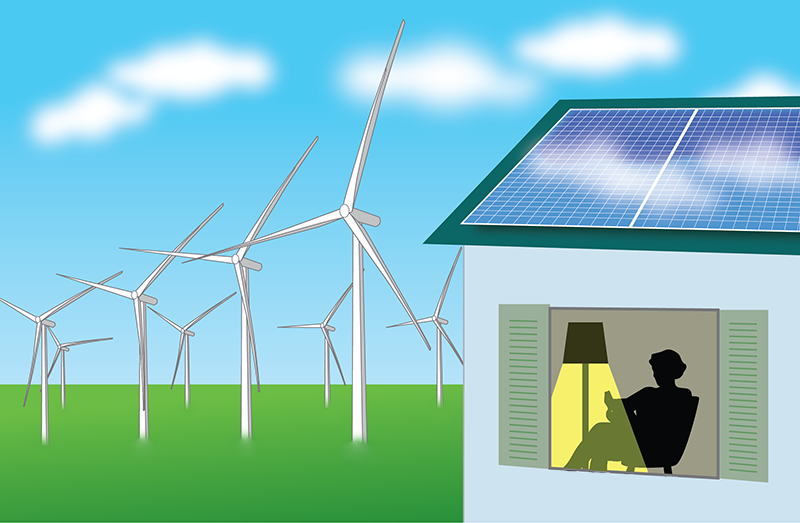
Solar Energy
Solar energy is a powerful and sustainable energy source. It harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity and heat. This clean and renewable energy helps reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Let's explore two main technologies used in solar energy: photovoltaic cells and solar thermal systems.
Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are made from materials like silicon. When sunlight hits the cell, it knocks electrons loose. This movement of electrons generates an electric current. Many cells form a solar panel. These panels can be installed on rooftops or large fields. They provide clean and green energy to homes and businesses.
Solar Thermal Systems
Solar thermal systems use sunlight to produce heat. This heat can then be used for various purposes. It can heat water for homes or generate steam for electricity. One common type is the solar water heater. It uses panels with tubes to absorb sunlight. The heated water flows through these tubes and into a storage tank. Another type is the concentrated solar power system. It uses mirrors to focus sunlight onto a small area. This concentrated heat can then produce steam to drive turbines and generate electricity.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is a clean and sustainable power source. It harnesses the wind to generate electricity. Large turbines capture the wind's kinetic energy. This energy is then converted into electrical energy. Wind energy is growing in popularity. It helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Aerodynamics Of Turbines
Wind turbines are designed with aerodynamics in mind. Their blades are shaped to capture wind efficiently. The shape allows the blades to spin at high speeds. This spinning motion drives a generator. The generator converts kinetic energy into electricity. The aerodynamic design reduces drag. It improves energy capture from the wind.
Wind Farm Design
Wind farms are groups of wind turbines. They are strategically placed to maximize energy production. Site selection is crucial. Wind speed and direction are carefully studied. Turbines are spaced to avoid interference. Proper spacing ensures optimal performance. Wind farms can be found on land and offshore. Offshore farms harness strong winds over the ocean.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power uses the energy of flowing water to produce electricity. This renewable energy source harnesses the principles of physics to generate clean, sustainable power.
Kinetic Energy Of Water
Dam And Reservoir Systems
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth's core. This renewable energy source is consistent and reliable. It provides a stable power supply, unlike solar or wind energy.
Heat Extraction Methods
There are several ways to extract geothermal heat. One common method is dry steam. This technique uses steam from underground to power turbines. Another method is flash steam. It involves pumping hot water under high pressure. The water turns to steam when pressure decreases. A third method is binary cycle. It uses hot water to heat another fluid. This fluid has a lower boiling point. It turns to vapor and drives the turbine. Each method suits different geothermal conditions.
Geophysical Properties
The Earth's geophysical properties affect geothermal energy. Temperature and pressure vary at different depths. High-temperature zones are ideal for geothermal plants. The type of rock also matters. Porous rocks allow water to flow easily. This is crucial for efficient heat transfer. Non-porous rocks can trap the heat. This leads to higher energy yields. Understanding these properties helps in site selection. It ensures the best use of geothermal resources.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from organic materials. Plants, wood, and waste are common sources. These materials store energy from the sun. Burning them releases that stored energy.
Biomass is a renewable energy source. It helps reduce greenhouse gases. It can also create jobs in rural areas. Using biomass is a step towards a cleaner planet.
Chemical Energy In Biomass
Biomass stores chemical energy. This energy comes from photosynthesis. Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. This energy stays in the plant material.
When we burn biomass, we release this stored energy. The energy can heat homes. It can also generate electricity. Biomass can be a sustainable energy source.
Conversion Technologies
Different technologies convert biomass into usable energy. One common method is combustion. Burning biomass produces heat. This heat can generate steam for electricity.
Another method is gasification. This process turns biomass into gas. The gas can then produce electricity or heat. Anaerobic digestion is also used. This process uses bacteria to break down organic material. It produces biogas, which can be used for energy.
Future Trends
Advancements in physics promise to improve renewable energy technologies. Efficient solar panels and wind turbines are becoming more common. These innovations reduce costs and increase energy output.
Innovations In Renewable Technologies
Integration With Smart Grids
Challenges And Solutions
Physics plays a crucial role in renewable energy. However, this field faces several challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges can pave the way for more effective solutions.
Intermittency Issues
Renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, are not always available. The sun doesn't shine at night, and the wind doesn't always blow. This intermittency can disrupt energy supply.
Imagine relying on solar power during a week of cloudy weather. Your energy needs might not be met. This is a significant problem for consistent energy delivery.
How can we solve this? One approach involves developing better forecasting models. Accurate predictions can help manage energy supply more effectively.
Energy Storage Solutions
Intermittency issues lead us to the need for energy storage. Storing energy for later use is vital. This ensures that we have power even when renewable sources are not producing.
Think about batteries. They store energy when it's plentiful and release it when needed. Advances in battery technology can significantly impact renewable energy reliability.
Consider Tesla's Powerwall. It stores solar energy for use at night. Innovations like this make renewable energy more practical for everyday use.
What other solutions exist? Beyond batteries, pumped hydro storage and compressed air energy storage show promise. Each method has its own benefits and challenges.
By addressing intermittency and improving storage, renewable energy can become a reliable source. What steps can you take to support these advancements?

Credit: physics.aps.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Renewable Energy Related To Physics?
Yes, renewable energy is related to physics. It involves principles of energy transformation, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism. Understanding these principles helps improve renewable energy technologies.
What Is Renewable Energy Explain In Physics?
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that replenish themselves, like sunlight, wind, and water. In physics, it involves converting these natural energies into usable forms, such as electricity. This process minimizes environmental impact and reduces reliance on finite resources.
What Is Green Energy In Physics?
Green energy in physics refers to power generated from renewable sources. Examples include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. These sources produce minimal pollution and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Green energy helps combat climate change and supports sustainable development.
What Are The Examples Of Renewable Resources In Physics?
Examples of renewable resources in physics include solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, and biomass. These resources are sustainable and can be replenished naturally.
Conclusion
Physics plays a vital role in renewable energy. It helps us understand how to harness natural resources like sunlight and wind. These insights lead to more efficient and sustainable energy solutions. As technology grows, physics will continue to drive renewable energy innovations.
This means cleaner air and a healthier planet for future generations. Embracing physics in renewable energy is not just important. It's essential. For a brighter, greener future, the science of physics is our guiding light.
.png)






0 Comments